
About
The NextGenPaper consortium of companies supports business and trade through its broad expertise in plastic waste avoidance. We provide a radically sustainable packaging solution launching a new era in packaging today - without excessive demands on their processes.
The tower of packaging power
This is NextGenPaper
NextGenPaper GmbH is a consortium of packaging and sales specialists based in Unterschleißheim near Munich. It was founded in 2022 to develop ecological, viable packaging solutions. NGP is led by a highly specialised team of entrepreneurs with practical experience in the packaging industry.
The tower of packaging power
This is NextGenPaper
NextGenPaper GmbH is a consortium of packaging and sales specialists based in Unterschleißheim near Munich. It was founded in 2022 to develop ecological, viable packaging solutions. NGP is led by a highly specialised team of entrepreneurs with practical experience in the packaging industry.

Florian Walch
CEO
Spezialist für Druck- & Verpackung

Jakob Kaikkis
CSO
VC- und Emerging Markets-Experte

Andreas Meyer
CTO
Experte für R&D, Process Engineering, Scouting

Jana Möltner
Social Media &
Sustainability Marketing

Florian Herrmann
CMO
Branding & strategische
Marketingberatung

Marco Schütte
CFO
Bank clerk and business graduate

Torsten Uhlig
Mitbegründer
Technology Development
Koryphäe für Beschichtungsverfahren

Doreen Zießnitz
Office Management & ERP
ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION MADE EASY
Our Mission
NextGenPaper is stepping up to become a leading provider of compostable and recyclable EU-compliant packaging solutions. With the latest generation of universally applicable tree-free multi-barrier papers, we provide businesses and consumers with the opportunity to effortlessly avoid plastic and packaging waste. Our sustainable and "user-friendly" products aim to promote environmental and climate protection worldwide.
We mean it
NextGenPaper and Sustainability
We are serious: NextGenPaper wants to assume the greatest possible social and ecological responsibility. Our start-up has already achieved the first milestone in this area with NGP multi-barrier papers made from sugar cane. And that’s just the beginning.
Example of CO2 emission calculation, Based on EU NORMEN 16258




Further sustainability aspects of NextGenPaper
- No additional cultivation areas
- Upcycling through the use of organic waste products
- No harmful emissions during processing
- Direct processing in local factories
- Low-emission transport by ship instead of truck
- Recyclable in the waste paper stream
- Support for factory employees in the Cauca Valley/Colombia (health and sanitation, early childhood care, income security and social support)
NAC SUSTAINABLY FUTURE-PROOF WITH NEXTGENPAPER
EU Sustainability Plans
The EU's future recycling requirements for packaging are the strictest in the world. With NGP products, manufacturers can meet these regulations without much effort. Already in 2018, the EU's Circular Economy Action Plan (Green Deal) set legally binding targets and deadlines for waste recycling and landfill reduction from 2025. As a result, recycling rates for plastic packaging have already risen to an all-time high of over 40% - three times higher than in the US and a quantum leap compared to most countries in Asia.
As part of the EU action plan presented in 2018. "Circular Economy" ("Green Deal"), legally binding targets and deadlines were set for waste recycling and landfill reduction from 2025. The EU measures are the most stringent in the world and have already pushed plastic packaging recycling rates to an all-time high of over 40%, three times higher than in the United States and a quantum leap compared to most regions in Asia.
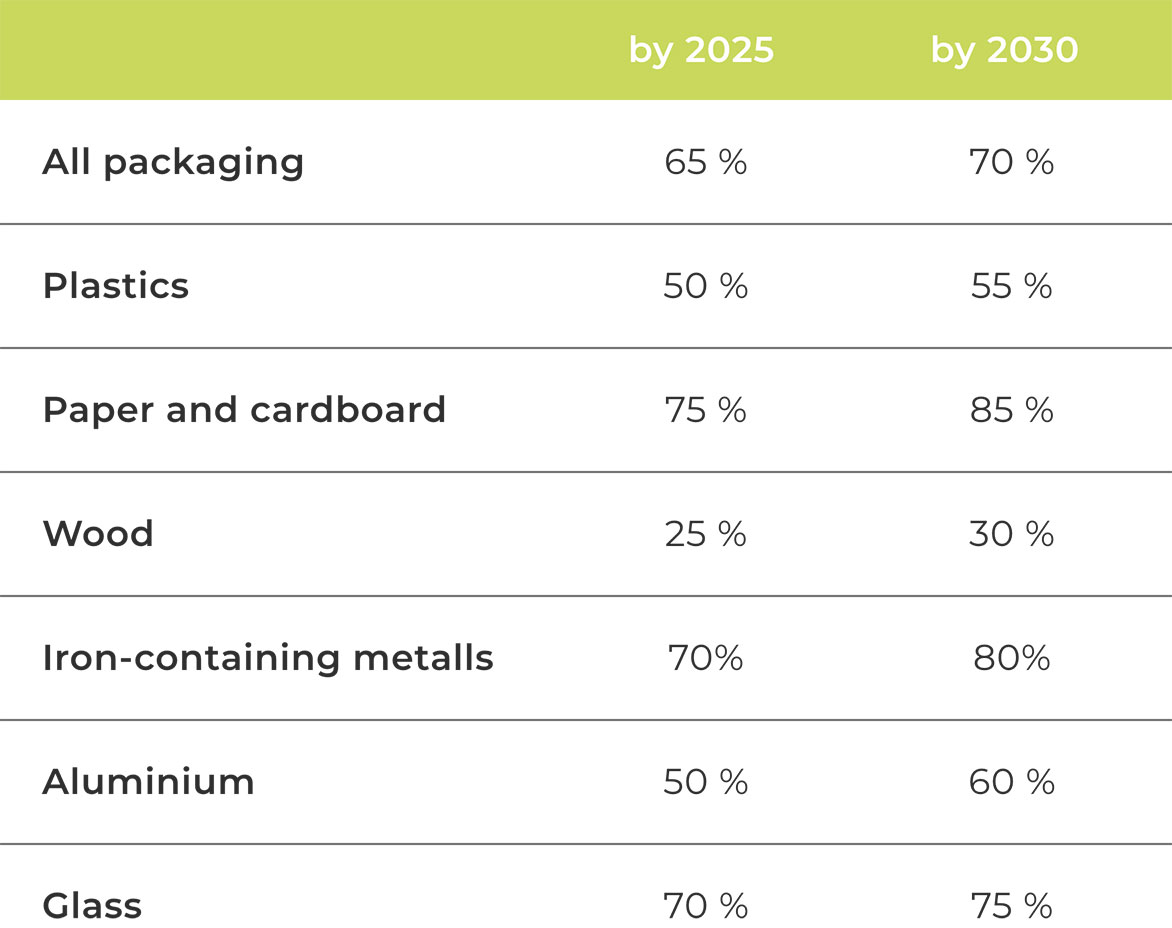
The EU Green Deal Strategy sets a common target for re-cycling of at least 55% of municipal waste by 2025, rising to 60% by 2030 and 65% by 2035. There is also a common EU recycling target of 65% of packaging waste by 2025 and 70% by 2030. There are separate targets for certain materials:
By 2035, no more than 10% of municipal waste must be sent to landfill. The EU Circular Economy Action Plan is expected to have a direct and immediate impact on a wide range of industries that produce or use plastic packaging. According to a tax report by Ernst and Young published in 2021, the UK, Spain and Italy are expected to be among the first to shift responsibility to manufacturers by introducing corresponding taxes on single-use plastic.
From March 2023, all companies selling food and drinks to French supermarkets have to display a recycling logo on labels as well as a QR code that provides shoppers with detailed information about packaging and recycling. In addition, fruit and vegetables sold in units of less than 1.5 kg may no longer be packaged in single-use plastic containers. Duty regulations or taxes on plastic packaging already exist in Spain, Portugal and Italy, as well as (in a slightly more relaxed version) in the UK. We expect to see many more local ordinances to engage industry, and possibly consumers, in the shift towards more sustainable packaging and consumption. NextGenPaper holds the key.
EU Recycling Targets for Packaging
Waste by 203
F.A.Q.
Here is a collection of the most frequently asked questions and the answers:
How does NextGenPaper differ from other suppliers of multi-barrier paper packaging?
The special feature of NGP multi-barrier papers is that the functional coating can be applied to any paper. In addition to the aforementioned kraft and sugar cane paper, customised papers are also possible. Furthermore, NextGenPaper is currently the only supplier of coated, tree-free papers. The tree-free sugar cane paper is our number 1 in terms of sustainability.
Is NGP packaging "organic"?
Organic is not a defined and protected term outside the food industry; it is therefore difficult to say whether NGP products are organic or not, because what are the criteria for that?! Is it about biodegradability? Then most of the packaging would be organic. Is NGP compostable? Not yet, but we are already working on home compostable packaging material.
How can NGP multi-barrier papers be printed?
NextGenPaper products are single-sided coated papers, which means the multi-barrier papers can also be printed on the non-coated side like "conventional" papers using, for example, offset, digital or screen printing processes.
Where can I get NGP multi-barrier paper?
NextGenPaper is available from our listed wholesalers. Please do not hesitate to contact us.
Do you need a new packaging machine to process NextGenPaper?
No, because NextGenPaper multi-barrier papers can be used on the usual machines after minor technical adaptations, such as, for example, a longer sealing time. We will be happy to assist you with the adjustment of your machines.
Why are NextGenPaper multi-barrier papers the environmentally friendly alternative to plastic packaging?
NGP multi-barrier papers are mainly used for disposable packaging. Compared to plastic, NextGenPaper can be easily disposed of in the waste paper stream and recycled. Disposable plastic packaging, on the other hand, is usually difficult or impossible to recycle.
Can NGP multi-barrier papers be tailored to specific functional requirements?
Yes. There are two different coatings that meet different barrier requirements. In addition, any paper can be coated.
For which applications is NGP multi-barrier paper made from sugar cane particularly suitable?
NGP multi-barrier papers based on sugar cane paper are our most environmentally friendly solution. Sugar cane paper is made from the waste of sugar production from sugarcane, making it a 100% tree-free upcycled material.
For which applications is NGP kraft paper particularly suitable?
NGP kraft paper is particularly suitable for packaging that requires especially high tear strength.

Glossar
B
Bagasse
Bagasse is a by-product left over from sugar production after the sugar canes have been pressed. The fibrous remains can be excellently processed into paper, among other things.
Barrier dispersion varnishes
A (barrier) dispersion varnish has an aqueous consistency. The coating is applied to the paper and then dries purely physically. This means that the water-containing parts dry out quickly without aids such as UV light.
Barrier properties
In order to protect the products in a package, various barriers are needed, e.g. against water, grease or oxygen. Which barriers a packaging material can fulfil and how well is referred to as barrier properties.
Biodegradable
A substance is biodegradable if it can be decomposed by microorganisms and/or bacteria. How long the decomposition process takes is not prescribed.
Bisphenol A (BPA)
Chemical compound mainly used in the production of various plastics. Included in the list of SVHC (Substances of Very High Concern) by ECHA due to its endocrine disrupting effects.
C
Circular economy
In a functioning circular economy, products are reused as long as possible. When a product has reached the end of its life, the raw materials remain in the economy and are used for other products. This minimises the amount of waste produced.
Coating process
Barrier papers like NextGenPaper get their special properties by being coated with a varnish or similar. Depending on the coating, this is applied to the paper in a different process.
Cobb (water absorption capacity) g/m2
Standardised Cobb value measurements can be used to determine how much water a material absorbs in a specified period of time. For this purpose, the test material is exposed to water for e.g. 1800 sec. exposed to water. Afterwards, the material is weighed. The material has also been weighed before the test. The lower the Cobb value, i.e. the increase in weight after the test, the higher the barrier property of the material against water.
Composite material
A composite material (also called composite material) refers to a material combination of two or more materials that are bonded together over their entire surface and cannot be easily detached from each other.
compostable
Compostable means that materials are biodegradable under certain conditions and within a defined period of time. A distinction is made here between composting in home composting or in industrial composting plants.
D
Deforestation-free
An EU regulation on deforestation-free supply chains is due to come into force in 2023. This is intended to curb global deforestation (clear-cutting and deforestation) caused by wood products. In future, every product imported into the EU must be verifiably traceable and deforestation-free.
Deinking process
In the deiking process, the printing inks are removed from the waste paper with the help of chemicals.
F
Fat barrier
Packaging with a grease barrier protects the packaged goods from greasy substances. The KIT value and the resistance to various oils precisely indicate the resistance value.
Flowpack
Flowpacks are a type of pouch packaging, also known as a tubular bag. Flowpacks are used frequently, especially in the food sector, as they are exceptionally stable and require only a small amount of material.
G
Green Deal
Under the EU's 2018 Circular Economy Action Plan ("Green Deal"), legally binding targets and deadlines have been set for waste recycling and landfill reduction from 2025. For example, a common EU target is a 70% recycling rate for packaging waste by 2030.
H
Halogen-free
Product total complies with limit values of 1500ppm halogens. Technically relevant halogens include fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine.
Heat sealability
Production of an adhesive bond under the influence of temperature without the addition of hot glue. The sealability of a coating lies in its properties.
HVTR (Hexane Vapor Transmission rate) g/(m2 +d)
23 °C/50 % examines the barrier properties of packaging materials against non-polar substances by measuring the amount of hexane vapour that penetrates the exposed surface from an evaporation chamber under controlled conditions. The lower the value, the higher the barrier against mineral oil-saturated hydrocarbons.
K
KIT (Oil & Grease resistance)
a method for determining the grease resistance of paper and board by testing the degree of surface repellency and/or anti-wicking properties of paper and board with organophobic materials. The higher the value, the better. The highest value is 12.
M
Monomers
A simple molecule with two or more binding sites through which it forms covalent bonds with other monomer molecules to form a macromolecule.
MOSH/MOAH
Mineral Oil Saturated Hydrocarbons, harmful chemical compound that accumulates in the liver and lymph
Mineral Oil Aromatic Hydrocarbons, chemical compound suspected of having a carcinogenic effect.
Multi-Barrier Lacquer
Lacquer layer that offers various barrier effects
Municipal waste
This includes waste from private households and comparable facilities (e.g. doctors' surgeries, kindergartens or care facilities).
O
OTR (Oxygen Transmission Rate) cc/(m2 +d)
23 °C/50 % evaluates the barrier properties or ability of different packaging materials to resist the permeation of oxygen by assessing the passage of oxygen molecules through a solid material over a period of time. The lower the value, the higher the oxygen barrier properties of the material.
Oxygen barrier
Packaging with an oxygen barrier protects the packaged goods from contact with oxygen. The OTR value of a material precisely indicates the resistance value.
P
Paper recycling
Recycled paper is a valuable raw material that can be excellently reused. In addition, recycled paper is significantly more environmentally friendly than virgin fibre paper. The production of recycled paper requires just 50% of the energy and 33% of the water compared to virgin fibre paper.
PE/PLA-free
PLA stands for polylactic acid, a synthetic polymer that belongs to the group of polyesters.
PE = Polyethylene, the best-known and most widely used plastic.
PFAS (per- and polyfl uroalkyl derivatives)
Large, complex group of synthetic chemicals consisting of long chains of carbon-fluorine compounds that are difficult to break down. Strong health effects on the immune system, thyroid, liver, lipid and insulin dysregulation, kidneys, reproduction, cancer, among others.
Plastic extrusion coating
Coating in which plastic, aluminium or paper carrier films are combined with a thermoplastic layer applied to them to form composites that are difficult to separate.
Plasticiser
Harmful substances that are added to brittle materials to make them more flexible. Negative effects on kidneys, liver, harmful to fruit and fertility.
Polymer coating
Also synthetic stiff coating. Coating of a material with a polymeric synthetic material.
Polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) coating
Highly effective chlorinated barrier coating polymer / barrier film, containing NIAS (non-intentionally added substances) which can easily migrate.
R
Recyclate
Substances or objects that consist wholly or partly of materials that have been recycled, e.g. plastics obtained from recycling processes.
T
Tree-free
Tree-free paper is made from alternative raw materials and does not contain fibres from trees (including recycled paper fibres from wood). Tree-free paper is, for example, sugar cane paper, as it is produced exclusively from the waste materials of the sugar cane plant.
V
Value chain
With the help of the value chain, the different manufacturing steps in a company are presented in an orderly sequence.
W
Waste management
According to Section 3 (14) of the KrWG, waste management is the provision, transfer, collection, transport, recovery and disposal of waste.
Water barrier
Packaging with a water barrier protects the packaged goods from contact with water. The Cobb value of a material precisely indicates the resistance value.
Water vapour barrier
Packaging with a water vapour barrier protects the packaged goods from contact with water vapour. The WVTR value of a material precisely indicates the resistance value.
WVTR (water vapour diffusion resistance) g/m2
23°C/85 % or 23 °C/ 50 % Also called water vapour transmission rate (WVTR), it is the amount of water vapour that penetrates a substance or material over a certain period of time. The lower the value, the lower the water vapour permeability - and the better the barriereffect ageinst water vapour